Comprehending and Mitigating Market-Wide Risks
The risk-return tradeoff is a principle fundamental to business, as investors typically seek higher returns for greater risks. Companies embrace this tradeoff to drive growth, innovation, and competitiveness by entering new markets, launching products, or adopting new technologies. These risks are crucial for achieving market leadership, adapting to market changes, and enhancing shareholder value.
Companies are exposed to various kinds of risks, which can differ significantly on an individual basis (across a company, industry, location, etc.). For instance, a firm involved in agriculture or manufacturing might be more severely exposed to commodity price risk, while those specializing in import/export could be more sensitive to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates. Such types of risks are called unsystematic or idiosyncratic risks, defined as risks unique to a single entity or industry and can typically be mitigated through diversification and hedging. However, not all risks can be easily managed, as some are inherent to the entire market or economy.
On the flip side, there is Systematic Risk, which affects a large number of assets or the entire economy. This type of risk includes changes in political landscapes, interest rates, or inflation, and cannot be mitigated through diversification alone, as it impacts all types of investments across the board. Monetary policy, directed by Central Banks such as the Federal Reserve in the U.S. or SAMA in Saudi Arabia influences factors that contribute to market-wide risk. Changes in these policies affect economic conditions like interest rates and inflation, impacting financial markets and investments broadly. Thus, they can lead to widespread effects across all asset classes, influencing market-wide risks in the economy.
Market-wide risks stem from macroeconomic factors and can impact an entire economy and a broad range of asset classes. Understanding these risks is critical for corporations to adjust their strategies effectively and manage potential impacts. Some of the key events that we have encountered in recent times, viewed as sources of market-wide risks, include:
- Inflation: This affects purchasing power and input costs. In extreme cases, hyperinflation can destabilize economies and investments.
- Monetary Policy and Interest Rate Changes: Controlled by Central Banks, these can significantly affect investment values and economic activities.
- Economic Cycles: These influence all businesses, typically affecting sales, profits, and stock prices.
- Geopolitical Events: These can disrupt markets by affecting trade routes, energy prices, and overall market stability.
Conscientious firms meticulously examine the sources of risks to which they are exposed and consistently uphold robust risk management guidelines. They place a critical emphasis on the identification, quantification, and management of market-wide risk within their strategies. By adopting this comprehensive approach, these firms effectively mitigate potential impacts on their operations, thereby safeguarding their long-term stability and promoting sustained growth.
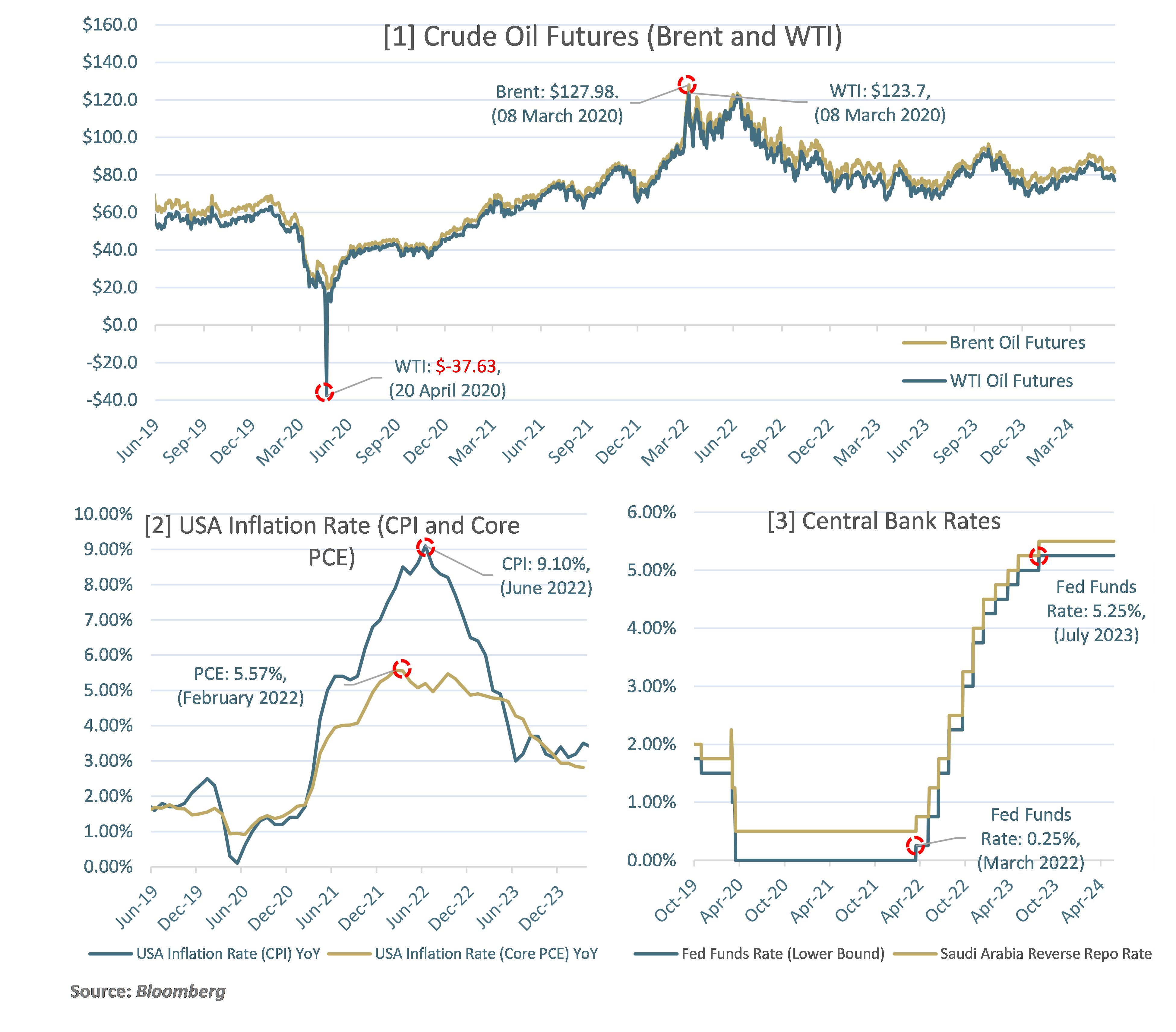
The charts above demonstrate certain instances of market-wide risks in recent times. Chart [1] displays the prices of crude oil futures over the last five years. On April 20, 2020, soon after the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, WTI futures fell to -USD 37.63 due to oversupply and a lack of storage capacity. Subsequently, WTI and Brent futures increased to their highest levels in 10 years as concerns over crude supply escalated due to the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Rising prices for crude and other commodities contributed to decades-high inflation, as can be seen in chart [2]. The annual inflation rate, measured through indicators like the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Index (the Federal Reserve’s preferred gauge of inflation in the U.S.), reached highs of 9.10% and 5.57% in June 2022 and February 2022, respectively. To combat these rising inflationary pressures, the Fed began hiking rates in March 2022, continuing through July 2023, raising them from 0% prior to the hikes to the target range of 5.25%-5.50%, as can be seen in chart [3].
Strengthening Client-Bank Relationships for Mitigating Market-Wide Risks
The relationship between corporates and the banking sector is pivotal for economic stability. Banks provide essential services such as financing, cash flow management, and market stability, which are crucial for businesses. By understanding and responding to economic fluctuations, banks help clients navigate financial challenges and opportunities. Additionally, banks play a key role in implementing monetary policy, and adjusting interest rates to achieve goals like managing inflation or stabilizing the currency.
Market-wide disruptions, such as rate hikes or financial crises, can profoundly impact both banks and their clients. Increased borrowing costs and financial instability can strain banks’ liquidity, leading to reduced lending capacity and stifled economic growth. For clients, this means higher costs for loans, reduced access to credit, and overall financial uncertainty. A weakened banking system can further destabilize the financial system, which in turn impacts clients’ financial security and confidence.
Given this interdependence, it is vital for banks to practice prudent governance and meet regulatory requirements. Equally important is the need for banks to understand and address client needs accurately, providing tailored solutions that enhance client resilience against economic fluctuations. When the economy is stressed, unsuitable financial solutions can lead to significant client losses, which also increases the credit risk for banks.
To mitigate market-wide risks, banks must implement robust regulatory measures such as stress testing, capital adequacy requirements, and comprehensive risk management protocols. These measures ensure banks remain resilient during economic shocks, protecting clients from cascading failures. By fostering strong customer relationships and adopting rigorous risk management practices, banks can secure their stability and contribute positively to the broader economy’s resilience, ultimately benefiting their clients.
Mitigating Market-Wide Risk
Both companies and financial institutions must develop and implement robust, carefully structured risk management strategies to safeguard against unsystematic and systematic risks. Our previous bulletin, ‘The Pillars of a Robust Hedging Policy‘, detailed how firms can establish and benefit from a hedging policy tailored to manage unsystematic risks.
To guard against market-wide risks, which impact the entire market or economy, companies can implement the following comprehensive strategies:
- Robust Liquidity and Risk Assessment: Maintain substantial liquidity reserves to ensure operational stability and meet financial obligations even during economic downturns. Employ advanced risk assessment tools, including stress tests and scenario planning, to evaluate the potential impact of different crisis scenarios on the firm’s portfolio. This proactive approach helps in preparing for and mitigating adverse effects during unexpected market conditions.
- Proactive Monitoring and Response: Continuously monitor macroeconomic trends and regulatory changes to anticipate and respond to emerging market-wide risks. This includes staying informed about global economic indicators, political changes, and Central Bank policies that could influence market dynamics. A vigilant approach enables firms to adapt quickly, safeguarding their operations and contributing positively to the stability of the financial system.
- Capital Adequacy and Revenue Stream Management: Ensure sufficient capital adequacy to absorb potential losses during periods of economic instability. Maintain strong capital buffers to withstand financial shocks and continue operations without severe disruptions. Regularly review and adjust capital structures to align with changing market conditions and regulatory requirements. Vary revenue sources and customer segments across different industries, credit ratings, and public/private sectors to spread risk and enhance overall financial stability and resilience.
Additionally, Companies must thoroughly understand their risk tolerance when discussing derivatives with financial institutions. It is essential for them to clearly define and select derivative instruments that align with their objectives and steer clear of complex and exotic alternatives that they may not understand and could lead to substantial risk exposure. Similarly, banks have a responsibility to carefully assess and safeguard client interests to prevent financial issues. This approach helps minimize risks and losses, especially during economic downturns, and reduces the likelihood of broader financial problems. Both companies and banks should commit to continuous risk assessment and education to navigate these complex financial instruments safely.
Market-wide risks pose significant challenges to companies, impacting their operations and financial stability across various economic sectors. It is imperative for firms to be thoroughly prepared to understand and address these risks, actively engage in ongoing risk assessment, and diligently monitor potential threats. They must develop comprehensive risk management strategies that effectively mitigate market-wide risks. By doing so, companies not only navigate through turbulent economic conditions more effectively but also safeguard their long-term interests and enhance stakeholder interests. Additionally, the ability to anticipate and adapt to these risks before they fully develop ensures that firms maintain a competitive advantage in a dynamic and interconnected global economy.




