Considerations for Proper Treasury Management in 2024
The year 2022 was expected to be the first year where markets are supposed to go back to what is considered “normal” after a covid era that required an ultra-low interest rates environment to stimulate markets and incentivize a persistently low inflation at the time. Yet, the year came with a new reality, where inflation in the US and other countries around the globe skyrocketed to 40-year high and peaked at 9.1% in the US while entering the double digits territory in other countries. During the same year, interest rates in the US increased by 400% as the Fed started to combat inflation to bring it down to the 2% target, and the journey continued through 2023 bringing rates to their highest level since 2007. These spikes were certainly reflected in our local market in the Kingdom as well, as displayed in the below chart that shows the Fed funds rate hikes for the past two years that went from approximately zero in the first quarter of 2022 to the current range of 5.25% to 5.50%. At the same time, the 3M SIBOR has followed suit and exceeded 6% this year to reach the highest level in more than 20 years.
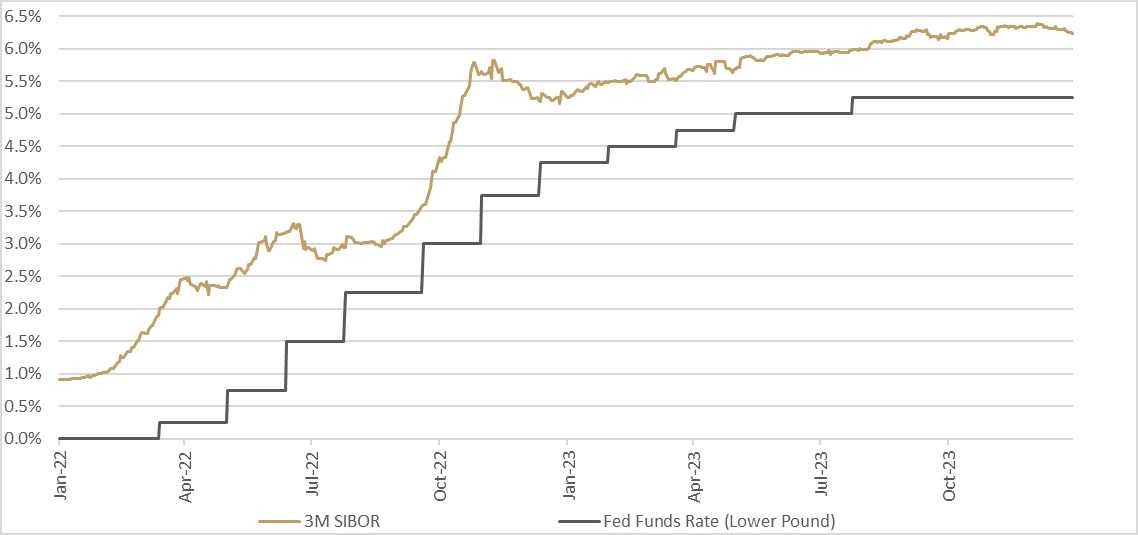
As we enter 2024, markets are preparing to embark on a change of direction by the US Fed, keeping rates constant in the latest three meetings after approximately two years of interest rate hikes, with the last increase that took place in July 2023. US Dollar, on the other hand, has been declining in recent months after the Fed pivoted into dovish sentiment. Prior to that, the greenback has been on the rise for the past two years in tandem with Fed rate hikes and the dollar index (DXY), which measure the US dollar against a basket of six major currencies, has reached a 20-year high mark in September 2022. Volatilities in currencies impact commodity prices that are additionally influenced by supply chain bottlenecks and geopolitical factors.
These changes combined require a vigilant stance by corporate treasurers as they manage their market risk exposures. As we start the new year, I will shed some light around three market risk considerations.
A Prolonged High Interest Rates Environment
Even though the US Fed has kept rates constant and indicated three cuts in 2024, there is an 83.5% probability that it will opt to keep rates constant in the first meeting of 2024 that take place on January 31st, according to the CME FedWatch Tool.
On the other hand, inflation has been slowing down and approching the Fed’s target as the latest inflation rate, measured by the consumer price index (CPI), came at 3.14%. Yet, the Fed is still determined to achieve its 2% target. The Fed chairman Jerome Powell stated that “Inflation is still too high, and a few months of good data are only the beginning of what it will take to build confidence that inflation is moving down sustainably toward our goal”.
Higher interest rates tend to increase the appeal of maintaining savings given the opportunity it offers of locking in high returns that were not available in the past decade. Yet, our focus here will be on the elevated borrowing costs. Prior to the current cycle of rates hikes, some businesses who entered into interest rate swap agreements may had thought it’s the wrong decision as they were hedging their interest rate exposure in a low interest rate environment and paying a negative carry (i.e., swap rate higher than reference rate). However, they now reap the benefits of such a decision which helped protect their P&L from markets volatilities, being the main goal of hedging. Having said that, corporates should not try to time the market and base their hedging decisions in reaction to market movements. Yet, such dicisions need to be based on defined Key Performance Indicatiors (KPIs), such as coverage ratios and fixed to floating debt ratio targets.
Managing Foreign Exchange Risk
Interest rate changes have a direct impact on currency exchange rates, and divergence in monetary policy stances or strategies by central banks can increase volatility. Earlier in 2023 for example, the Euro hit 15-year high against the Japanese yen, where the European central bank (ECB) has been raising rates similar to what is happening in the US and the bank of Japan (BoJ) was sticking to its dovish monetary policy.
For an entity to manage its currency risk exposure, it needs to identify the type of its currency risk. Translation currency risk will have an impact on the balance sheet and happens for companies who own foreign assets that are reported on their financials. Transaction currency risk, on the other hand, as the name implies, happens when there are cash flows in a foreign currency and will impact an entity’s P&L. It is important to define the currency risk exposure type, have threshold limit and target hedge ratio in order to properly manage FX exposure, and mitigates negative impact of volatilities.
Volatility in Commodities Prices
There are several factors that cause fluctuations in commodity prices. Supply chain is one of these factors, where unfortunately it seems to be a theme in the last couple of years that supply chains continue to face different kind of disruptions, from Covid lockdowns to geopolitical unrests as the Russia-Ukraine conflicts. These factors lead to increases in commodities prices and amplify the impact of increased inflation rates. Volatility can have a serious impact on business operations as it may limit access to some materials, cause cash flows fluctuations, and expose the P&L to increased volatility via the cost of goods sold (COGS), which would eventually impact profit margins and profitability.
Protection against volatilities in commodities prices can be achieved via derivatives instruments as forwards, futures, swaps, and options or else via fixing prices with suppliers to achieve price certainty over the agreed period. Either way, an entity needs to have a clear risk management framework and objectives with regard to managing commodity prices risk.
Bottom Line
Navigating through the ever-changing market dynamics need to be guided by a hedging policy. One which defines an entity’s risk management objectives and address its goals. Whether an entity aims to protect itself from an elevated borrowing costs or an unstable currency exposure, it is essential that the policy includes systematic approaches to identifying, measuring, and managing the relevant financial risks in a manner that aligns with the entity’s strategic financial targets and operational capabilities.




